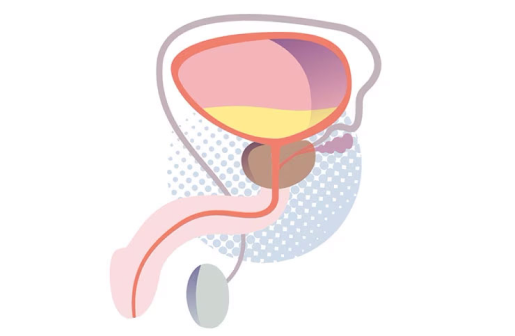
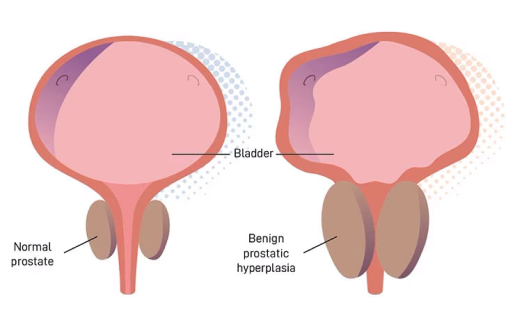
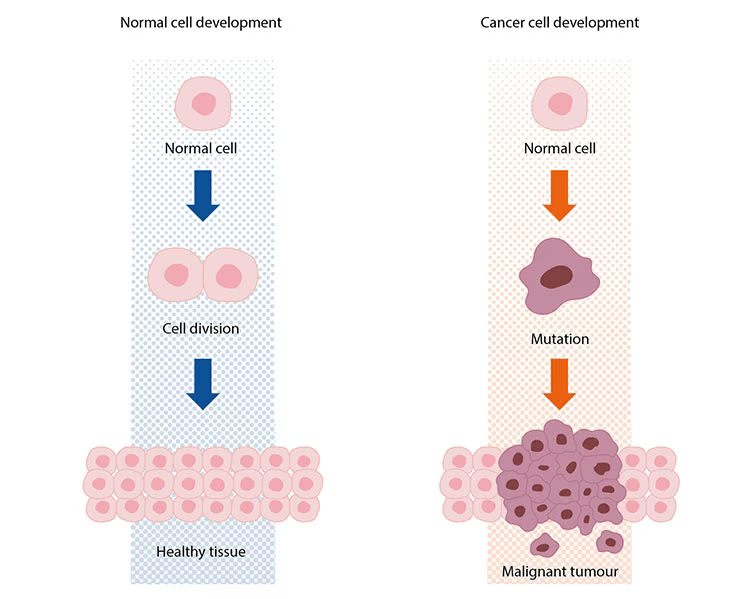
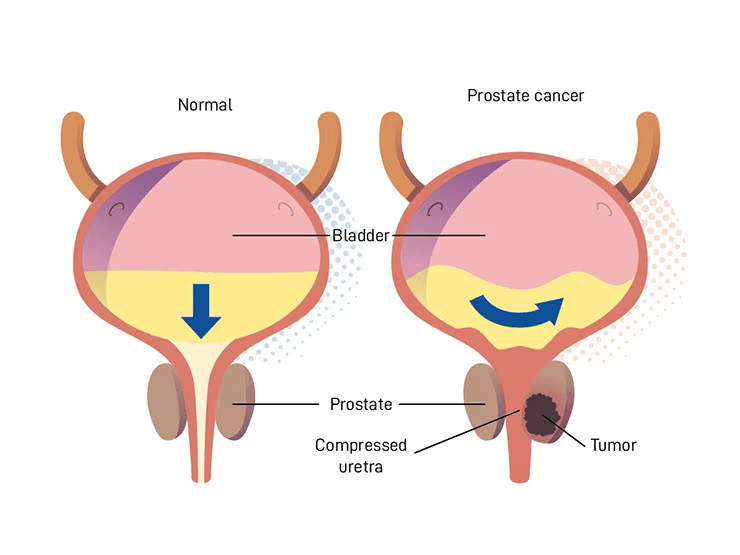
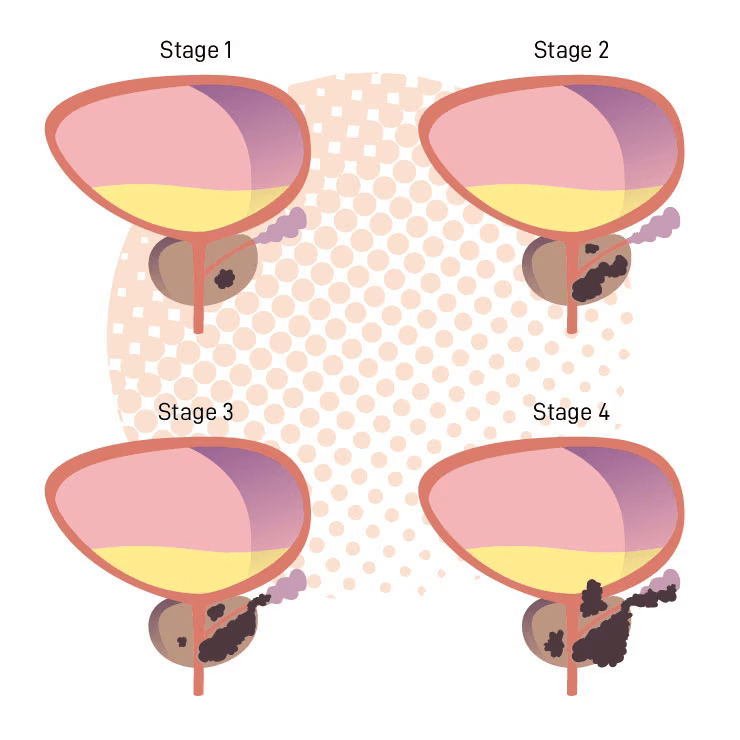
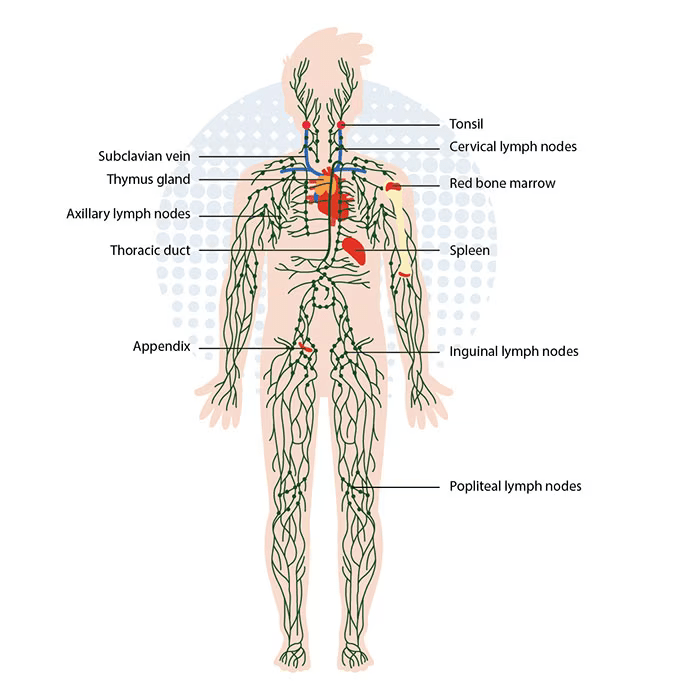
All biological organisms including plants and animals are made up of tiny components called cells. Each cell has a biological code called DNA and this code is organised into a series of genes which contain the information needed for the organism to function and also determine a variety of the organisms’ characteristics including height, weight, eye colour, skin colour and the timing for cells to divide or to stop dividing.
Each organism begins as a single cell, and multiplies by giving birth to new cells, and then either stops dividing at some point or dies based on its built-in genetic code. All of the information contained in the genes is passed on to descendant cells. Certain genes may have mutations or mistakes in their building blocks which may cause the cell's working program to be disrupted and cause it to behave abnormally. These abnormalities are either naturally corrected by the body’s fail-safe mechanisms (immune system) or they can cause the cell to die spontaneously.