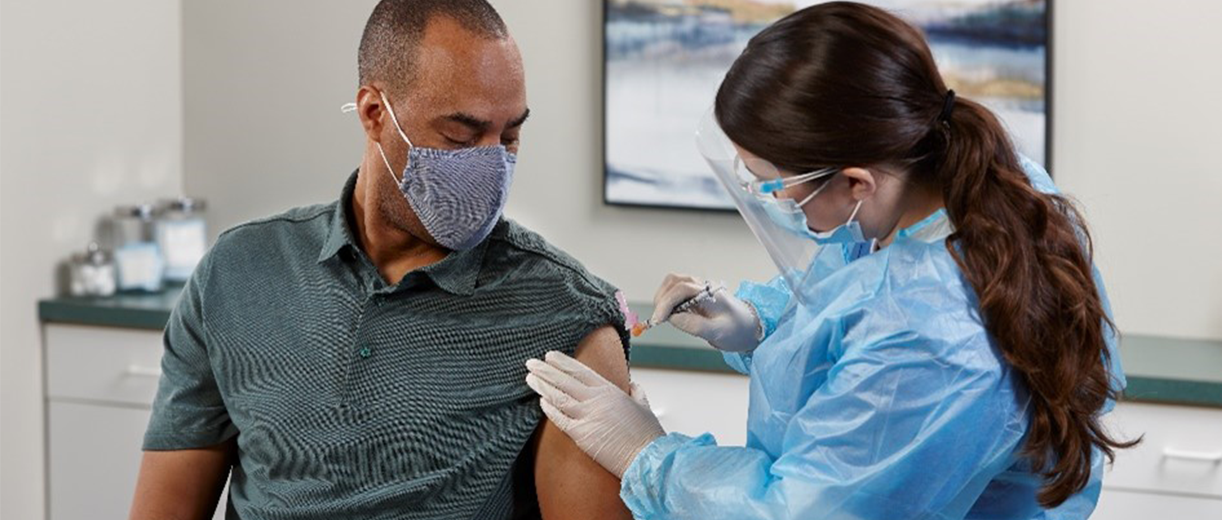
Straight to the point: how to better manage needle phobia
Are you having trouble administering injections to patients with needle phobia?
The fear of needles is frequent. An estimated 63% of children and 24% of adults reported experiencing needle phobia or trypanophobia according to the results of a survey published in 20121.
High levels of anxiety contribute to needle phobia2.
High anxiety typically manifests itself as a severe apprehension of needle procedures2.
Needle phobia may cause your patients to delay or even avoid necessary medical procedures3.
This can compromise inpatient and outpatient treatment4
From fear to pathological disorder
Although less frequent than the fear of needles, pathological needle phobia is an extreme psychiatric disorder3. Its symptoms include stimulus avoidance, a diphasic vasovagal response, an increase then sudden decrease in blood pressure, which may lead to fainting3.
The sight of blood may trigger this vasovagal response2. A past needle-related traumatic event involving bleeding is one factor that can lead to developing this phobia3.
Learn about Helping patients and the planet, one injection at a time!
Needle size: a factor in needle phobia?
One of the major factors for developing needle phobia is pain2. Frequency of pain has been shown to vary significantly according to needle gauge5.
In a 2020 global survey of 875 clinicians in 19 countries, approximatively 80% of clinicians reported using thin-wall needles at least monthly and believe there are benefits, including the option to use a finer gauge needle, which could provide a better, less painful patient experience6.
The possibility of bleeding following injection has also been shown to decrease as needle diameter decreases5.
Learn about Feeling down after a needlestick injury? You’re not alone
Six recommendations to help mitigate needle phobia in your patients
- Be aware of the psychosocial factors leading your patients to develop a fear or phobia of injections3,7
- Tailor your fear mitigation strategies to each patient7
- Explain the procedure and what will happen7
- Distract fearful patients with toys or videos7
- Decorate syringe barrels with colourful stickers (e.g., musical notes, smiley faces or flowers)4
- Use a smaller gauge to help reduce pain5
Thin-wall needles have a narrower steel wall, which enables the use of a smaller gauge needle8.
To learn more about the advantages of thin-wall needles, watch the video and download the brochure below.
References
- Taddio A, Ipp M, Thivakaran S, et al. Survey of the prevalence of immunization non-compliance due to needle fears in children and adults. Vaccine. 2012;30(32):4807-4812. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.05.011
- McMurtry CM, Pillai Riddell R, Taddio A, et al. Far From “Just a Poke”: Common Painful Needle Procedures and the Development of Needle Fear. Clin J Pain. 2015;31(10 Suppl):S3-11. doi:10.1097/AJP.0000000000000272
- McLenon J, Rogers MAM. The fear of needles: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Adv Nurs. 2019;75(1):30-42. doi:10.1111/jan.13818
- Kettwich SC, Sibbitt WLJ, Brandt JR, Johnson CR, Wong CS, Bankhurst AD. Needle phobia and stress-reducing medical devices in pediatric and adult chemotherapy patients. J Pediatr Oncol Nurs. 2007;24(1):20-28. doi:10.1177/1043454206296023
- Gill HS, Prausnitz MR. Does needle size matter? J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2007;1(5):725-729. doi:10.1177/193229680700100517
- BD Data On File, BD-AD-5540 Andrew Bridges Preference Claim Memo, May 2021.
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Needle Fears and Phobia – Find Ways to Manage. Children’s Mental Health. Published April 11, 2022. Accessed October 17, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/childrensmentalhealth/features/needle-fears-and-phobia.html
- BD Data On File, C-2748 Flow Rate Memo Andrew Farinella, July 2021.
This list of references to third-party peer-reviewed material and the sites they are hosted on are provided for your reference and convenience only, and do not imply any review or endorsement of the material or any association with their operators. The Third-Party References (and the Web sites to which they link) may contain information that is inaccurate, incomplete, or outdated. Your access and use of the Third Party Sites (and any Web sites to which they link) is solely at your own risk.
BD-75473